आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी, जिसे मोसेली की आवर्त सारणी भी कहा जाता है, एक व्यवस्थित तरीके से रासायनिक तत्वों का वर्गीकरण है। इसे ब्रिटिश वैज्ञानिक हेनरी मोसेली (Henry Moseley) ने 1913 में प्रस्तुत किया था।
The modern periodic table, also known as Moseley’s periodic table, is a systematic classification of chemical elements. It was introduced by British scientist Henry Moseley in 1913. आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी || Modern Periodic Table
आधुनिक आवर्त नियम (Modern Periodic Law)
“तत्वों के भौतिक और रासायनिक गुण उनके परमाणु क्रमांक (Atomic Number) के आवर्त फलन होते हैं।”
मतलब, तत्वों को उनके परमाणु क्रमांक के आधार पर व्यवस्थित किया जाता है, न कि परमाणु द्रव्यमान के आधार पर (जैसा कि मेंडलीफ की सारणी में था)।
“The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers.”
That is, the elements are arranged based on their atomic numbers, not atomic masses (as in Mendeleev’s table).
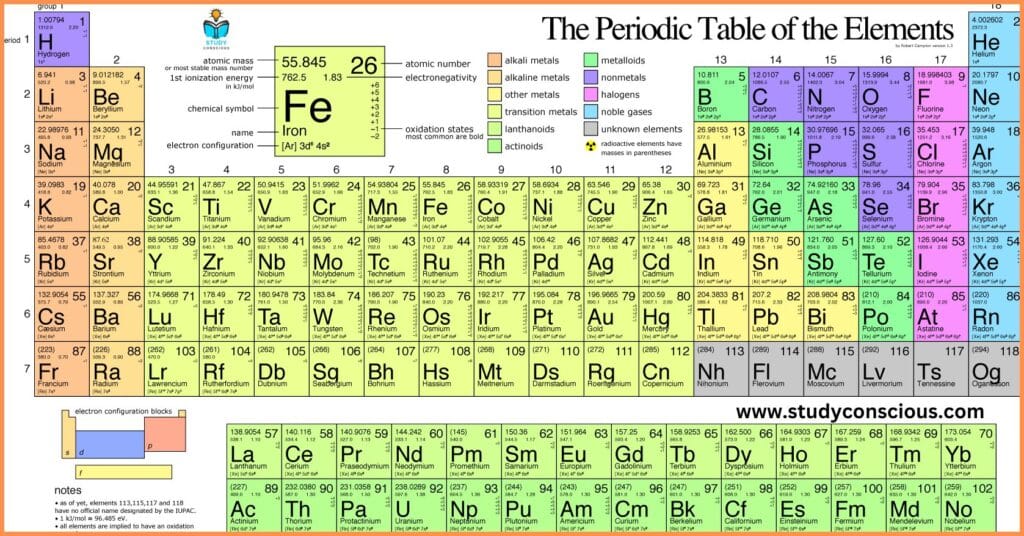
आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी की संरचना (Structure of the Modern Periodic Table)
| कुल तत्व | 118 (अब तक खोजे गए) |
|---|---|
| आवर्त (Periods) | 7 (क्षैतिज पंक्तियाँ) |
| गुणक (Groups) | 18 (ऊर्ध्वाधर स्तंभ) |
1. आवर्त (Periods) – 7 क्षैतिज पंक्तियाँ
- प्रत्येक आवर्त में तत्वों की संख्या भिन्न-भिन्न होती है।
The number of elements in each period is different. - निचले दो आवर्त (6 और 7) में लैन्थेनाइड और एक्टिनाइड श्रेणियाँ शामिल होती हैं।
The lower two periods (6 and 7) contain the lanthanide and actinide series.
2. गुणक (Groups) – 18 ऊर्ध्वाधर स्तंभ
- प्रत्येक गुणक में एक जैसे रासायनिक गुण वाले तत्व होते हैं।
Each factor contains elements with similar chemical properties. - मुख्य रूप से चार वर्ग होते हैं:
There are mainly four classes:- क्षारीय धातु (Alkali Metals) – समूह 1
- क्षारीय मृदा धातु (Alkaline Earth Metals) – समूह 2
- हैलोजन (Halogens) – समूह 17
- निष्क्रिय गैसें (Noble Gases) – समूह 18
आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी की विशेषताएँ (Features of Modern Periodic Table)
- परमाणु क्रमांक के अनुसार वर्गीकरण – तत्व परमाणु क्रमांक के अनुसार क्रमबद्ध होते हैं, जिससे उनकी स्थितियाँ निश्चित रहती हैं।
Classification according to atomic number: Elements are arranged according to atomic numbers, so that their positions remain fixed. - आवर्तता का सिद्धांत – समान गुण वाले तत्व निश्चित अंतराल (आवर्त) पर दोबारा प्रकट होते हैं।
Principle of Periodicity – Elements with similar properties appear again at definite intervals (periods). - ब्लॉकों में विभाजन – तत्वों को चार ब्लॉकों में विभाजित किया गया है:
Division into blocks – The elements are divided into four blocks:- s-ब्लॉक (क्षारीय और क्षारीय मृदा धातुएँ)
- p-ब्लॉक (हैलोजन और निष्क्रिय गैसें)
- d-ब्लॉक (संक्रमण धातुएँ)
- f-ब्लॉक (लैन्थेनाइड और एक्टिनाइड श्रेणी)
- संक्रमण और आंतरिक संक्रमण तत्वों की सही स्थिति – d-ब्लॉक और f-ब्लॉक तत्वों की उचित स्थिति निर्धारित की गई।
Correct position of transition and inner transition elements – Proper position of d-block and f-block elements determined. - नए तत्वों को जोड़ने की क्षमता – नई खोजे गए कृत्रिम तत्वों को आसानी से जोड़ा जा सकता है।
Ability to add new elements – Newly discovered artificial elements can be easily added.
Here’s a Periodic Table with Element Names and Electronegativity (Pauling Scale) in table format:
Lanthanides & Actinides
| Element | Electronegativity | Element | Electronegativity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lanthanum (1.10) | Neodymium (1.14) | Promethium (-) | Samarium (1.17) |
| Europium (1.20) | Gadolinium (1.20) | Terbium (1.20) | Dysprosium (1.22) |
| Holmium (1.23) | Erbium (1.24) | Thulium (1.25) | Ytterbium (1.10) |
| Lutetium (1.27) | Thorium (1.30) | Protactinium (1.50) | Uranium (1.38) |
| Neptunium (1.36) | Plutonium (1.28) | Americium (1.30) | Curium (1.30) |
| Berkelium (1.30) | Californium (1.30) | Einsteinium (-) | Fermium (-) |
Notes:
- Electronegativity values are based on the Pauling scale.
- Noble gases (Group 18) generally do not have electronegativity values since they do not commonly form compounds.
- Elements with “-” do not have a well-defined electronegativity due to lack of data or instability.
आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी के लाभ
✅ तत्वों का स्पष्ट वर्गीकरण।
✅ तत्वों के गुण आसानी से समझे जा सकते हैं।
✅ नए तत्वों को व्यवस्थित ढंग से जोड़ा जा सकता है।
✅ तत्वों के रासायनिक और भौतिक गुणों की भविष्यवाणी की जा सकती है।











